What is Address Reuse?
Address reuse in cryptocurrency transactions reduces privacy and anonymity.
Reuse of an identical cryptocurrency address for multiple input/output transactions potentially creates an opportunity for blockchain observers to attribute that address — and possibly an entire string of intervening addresses — to a particular person.
What Does Address Reuse Look Like?
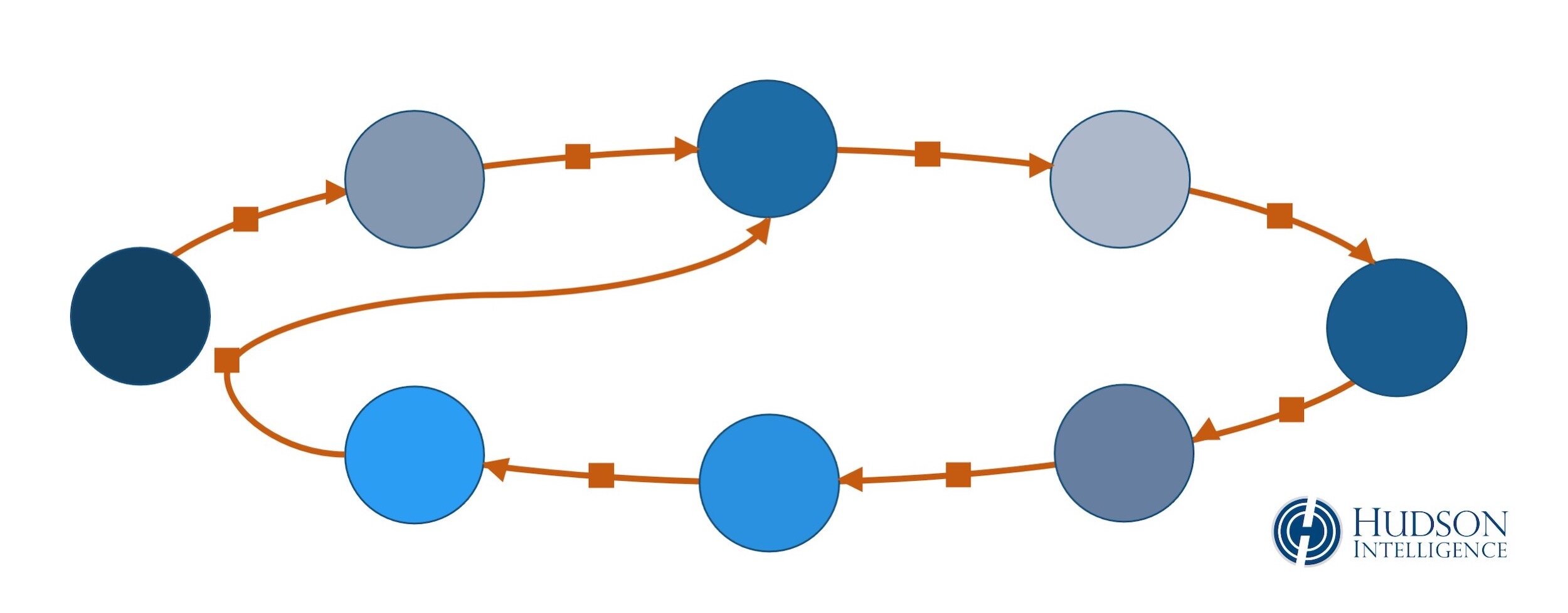
The diagram below is a depiction of address reuse, similar to how such data is rendered by cryptocurrency intelligence tools, which convert accounting entries from blockchain ledgers into visual maps or flowcharts.
This example shows one-to-one transfers across a series of intermediary addresses as digital money moves from one address to the next in a loop-like rotation. At the end, an address seen earlier in the cycle is reused as an output address to receive the final transfer.
At minimum, an analyst would likely attribute the final six addresses within this loop to the same person. Linking multiple addresses to the subject of an investigation can significantly expand the field of evidence.
In an actual blockchain investigation, this diagram and its underlying data would include hashes, fees, time/date stamps, attribution data, and other relevant information.
Why do Investigators Focus on Address Reuse?
A key challenge for blockchain tracing is identifying which branch of any transaction represents addresses owned and controlled by the subject of the investigation, as opposed to a third-party payment or exchange addresses. These include existing addresses in the subject’s wallet, and change addresses automatically generated during transactions.
Money launderers and cryptocurrency fraudsters use various methods to obscure their identities and assets, including peel chains and layering, which can create complex loops of opaque transfers. By reusing a known cryptocurrency address across multiple transactions, they send a signal that all intervening addresses along the same branch – which could contain dozens or hundreds of hops – are controlled by the same subject.
Consult an Investigator
Hudson Intelligence assists law firms, businesses, public agencies and investors with cryptocurrency investigations and due diligence. Every investigation is led by a Cryptocurrency Tracing Certified Examiner (CTCE) and Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE). If you would like to discuss a potential investigation, please complete the form below. We also suggest reviewing our FAQ.